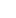
In modern industrial manufacturing, the demand for component precision is increasingly high, and this is inseparable from a key machine tool: the grinder. While many may be more familiar with lathes and milling machines, grinders are the unsung heroes that achieve ultra-high surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
A grinder is a precision machine tool that uses a grinding wheel as a cutting tool to grind workpiece surfaces. Its core function is to remove material to achieve the required dimensional tolerances and surface quality by rotating the grinding wheel at high speed, contacting the workpiece surface, and cutting with an extremely small depth of cut.
Compared to traditional turning and milling, grinding offers the following significant advantages:
- High Precision: Easily achieving micron-level dimensional accuracy is the foundation for high-quality products.
- High Finish: The finished surface achieves an extremely high degree of surface finish (roughness), meeting stringent surface requirements.
- Hard Material Machining: It can effectively process heat-treated, high-hardness materials, which is difficult for other cutting tools to achieve.

Content
Types and Applications of Grinding Machines
Grinding machines can be divided into several types based on the workpiece and structural characteristics. Each type has specific applications and core functions:
- Cylindrical Grinders: Primarily used for grinding the outer surfaces of cylindrical and conical workpieces. Typical applications include shafts, precision rollers, and crankshafts.
- Internal Grinders: Specialized for grinding the inner surfaces of cylindrical and conical workpieces. Typical applications include internal bore machining of engine cylinder bores, high-precision sleeves, and other applications.
- Surface Grinders: Used for grinding flat and formed surfaces on workpieces, they are key equipment for achieving high-precision flat surfaces. Typical applications include surface grinding of guide rails, molds, and gauges.
- Centerless Grinders: Eliminate the need for a chuck or center hole and are suitable for high-volume continuous production. Typical applications include small-diameter parts such as piston pins, needle rollers, and rollers.
- Tool Grinders: Specialized machines used for sharpening and refining the edges of various cutting tools, such as drills and milling cutters.
Applications and Importance of Grinding Machines
Grinding machines are used throughout industry and are a critical component of precision manufacturing. They are widely used in fields requiring extremely high precision, including automotive, aerospace, mold making, bearings, hydraulic components, and electronics. Technological advances have made grinding complex surfaces more efficient and precise.
From tiny precision parts to large industrial components, grinding machines are essential precision machine tools for ensuring product quality and improving performance. Whether demanding the most demanding materials or requiring precise dimensions, grinding machines are a powerful tool for achieving the ultimate precision in modern machining centers.
 0086-15068518279 (Chinese)/001-5416026691 (English)
0086-15068518279 (Chinese)/001-5416026691 (English) 

 EN
EN
 中文简体
中文简体