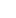
To use a CNC cylindrical grinding machine, you first need to clamp the workpiece and set the tool. Then, input or call the machining program (G-code) into the CNC system. Set the grinding wheel speed, feed rate, and cooling system on/off via the control panel. Finally, start the automatic cycle mode for precision grinding. The core operation is ensuring precise matching between the workpiece axis and the grinding wheel's movement trajectory to achieve micron-level dimensional tolerances and surface roughness requirements.
Content
Understanding the Core Components of a CNC Cylindrical Grinding Machine
Before delving into the operational process, understanding the basic structure of precision grinding equipment is essential. A CNC cylindrical grinding machine mainly consists of a bed, headstock (driving the workpiece rotation), tailstock, grinding wheel head (mounting the grinding wheel), and the crucial CNC numerical control system.
CNC System: Responsible for controlling the linkage between the X-axis (grinding wheel feed) and Z-axis (table longitudinal movement).
Servo Drive: Ensures the stability of feed accuracy, directly affecting the effect of external cylindrical grinding.
Detailed Operating Procedures for a CNC Cylindrical Grinding Machine
1. Power-On and Origin Return
After powering on, a "zero return" operation must be performed. This is to allow the CNC grinding machine to establish its mechanical coordinate system, ensuring the absolute accuracy of subsequent machining paths.
2. Workpiece Clamping and Alignment
Select center hole support or chuck clamping according to the workpiece shape. Use a dial indicator to check the radial runout of the workpiece to ensure the smoothness of the rotation axis.
3. Programming and Input
Import the machining program via manual data input (MDI) or USB flash drive. The program must include:
- Grinding wheel linear speed settings
- Segmented feed parameters for rough grinding, fine grinding, and sparkless grinding
- Compensation data for dressing the grinding wheel
4. Tool Setting and Workpiece Coordinate Setting
Determine the reference position of the grinding wheel and the workpiece surface using a tool setter or the "spark test" method. This step determines the initial accuracy of CNC machining.
5. Automatic Machining and Cooling
Start the coolant nozzle (aligning it with the grinding point) and click "Cycle Start". Operators must monitor the grinding process through sound and spark monitoring.

Core Elements for Improving Machining Quality in CNC Cylindrical Grinding Machines
Simply relying on automation programs is insufficient when operating CNC cylindrical grinding machines. To achieve sub-micron precision machining, in-depth optimization is necessary in three dimensions: wheel condition, thermal deformation control, and positioning datum.
1. Precision Dressing and Maintenance of Grinding Wheel Characteristics
The microstructure of the grinding wheel directly determines the surface finish of external cylindrical grinding. While the CNC system can control the feed, it cannot automatically change the dulling state of the grinding wheel.
Technical Details: The sharpness of the diamond dresser must be maintained. The longitudinal feed rate during dressing should be flexibly adjusted according to the requirements of roughing and finishing grinding—a larger feed rate can be used for rough dressing to improve cutting efficiency, while a very small feed rate is required for finishing to induce micro-grinding edges on the grinding wheel surface.
Value: Regular and scientific dressing effectively prevents surface chatter marks (wavy lines) and significantly reduces the risk of grinding burns.
2. Dynamic Thermal Stability and Coolant Management
Grinding is essentially a high-energy removal process that generates significant grinding heat. In precision grinding equipment, thermal deformation is a "hidden killer" leading to dimensional deviations.
Technical Details: Coolant not only cools the surface but also washes away grinding debris and prevents wheel clogging. A constant-temperature cooling system is recommended to ensure that the coolant temperature fluctuates in sync with the machine bed temperature. Simultaneously, the coolant nozzle angle must be precisely aimed at the "wedge-shaped area" of the grinding zone to maximize heat exchange.
Value: Good thermal balance management effectively controls the radial thermal expansion of the workpiece, ensuring dimensional consistency remains within minimal tolerances during continuous machining of a batch of parts.
3. Physical Datum and Center Hole Integrity
For CNC cylindrical grinding machines using center supports, the workpiece's center hole is its rotational geometric datum.
Technical Details: Before clamping, the center holes at both ends of the workpiece must be rigorously inspected for dents, oxide scale, or chips. It is recommended to use high-precision, ground centers and apply a dedicated high-pressure grease to the contact surfaces. If the center hole has a geometric error of 0.01mm, after rotational magnification, the error reflected in the workpiece roundness may increase exponentially.
Value: Ensuring the cleanliness and roundness of the reference position is fundamental to achieving high coaxiality and high roundness machining, and is also a prerequisite for maximizing the repeatability of the CNC system.
Safety Precautions: When operating automated grinding equipment, appropriate protective equipment must be worn. It is strictly forbidden to open the safety door while the grinding wheel is rotating at high speed, and the grinding wheel should be checked regularly for cracks to prevent the risk of explosion under high-speed rotation.
Proficient use of CNC cylindrical grinding machines requires not only an understanding of software programming, but also sensitivity to mechanical assembly and process parameters.
 0086-15068518279 (Chinese)/001-5416026691 (English)
0086-15068518279 (Chinese)/001-5416026691 (English) 

 EN
EN
 中文简体
中文简体